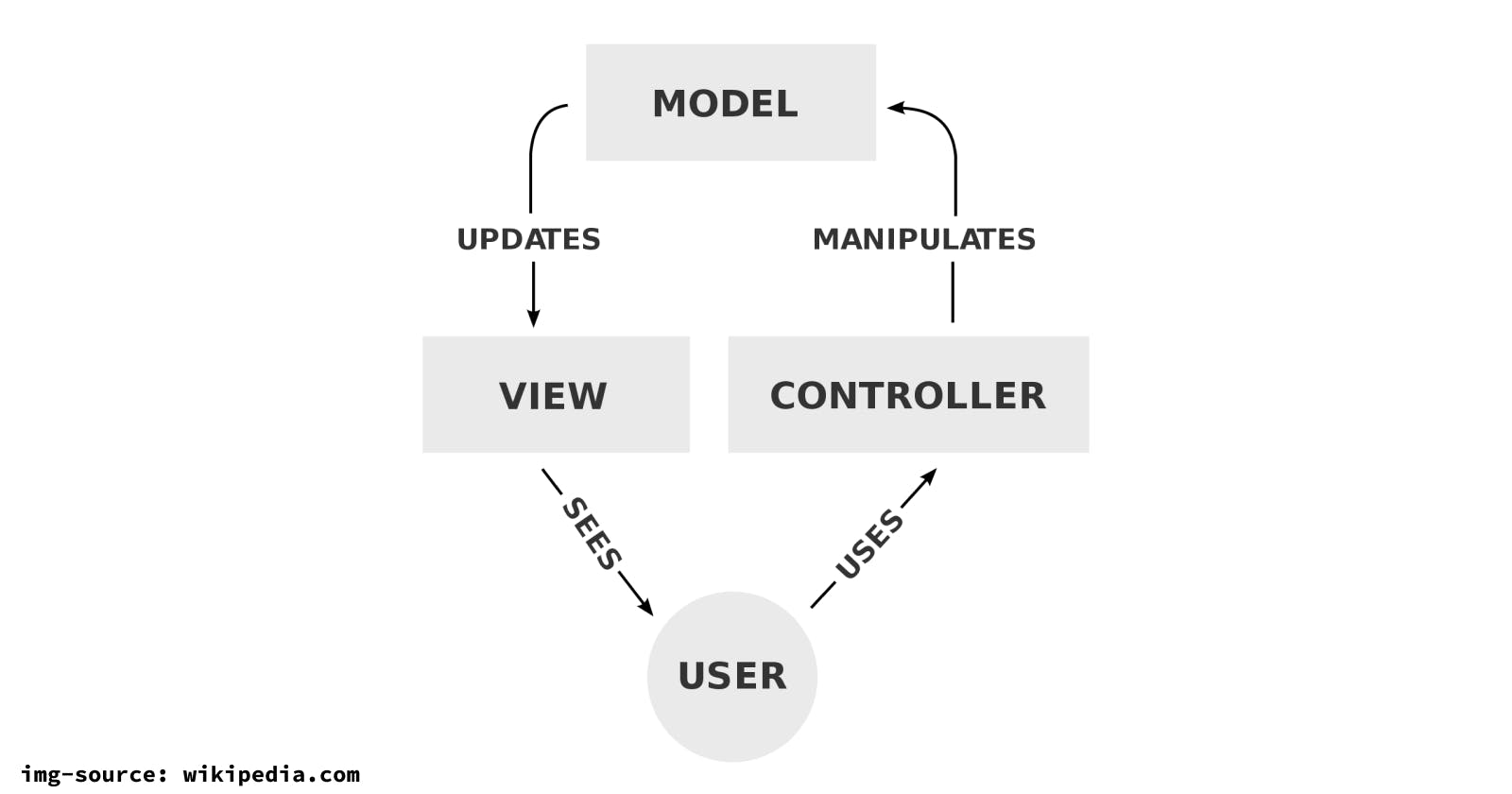
MVC, or Model-View-Controller, is a popular design pattern used in software development to separate an application's concerns into three distinct components: the model, the view, and the controller. Understanding this pattern is crucial for creating efficient and maintainable code.
In this article, we'll explore the MVC pattern and its role in software development.
What is MVC?
MVC is a design pattern used to separate an application's concerns into three distinct components: the model, the view, and the controller. This separation of concerns enables developers to create maintainable, modular, and scalable applications.
How does MVC work?
Model
represents the data and the business logic of the application. It is responsible for the storage, retrieval, and manipulation of data. The Model ensures that the data is consistent and that it follows the rules and constraints of the application.
View
responsible for the presentation of data to the user. It is part of the application that the user interacts with. The View is responsible for displaying data in a user-friendly format, and for accepting user input.
controller
acts as the intermediary between the Model and the View. It receives user input from the View, processes it using the Model, and then sends the updated data back to the View. The Controller also manages the flow of data between the Model and the View, ensuring that they remain synchronized.
Advantages of MVC
There are several advantages to using the MVC pattern in software development:
Separation of concerns: The MVC pattern separates an application's concerns into three distinct components, making it easier to develop, test, and maintain.
Scalability: Because the MVC pattern separates an application's concerns, it's easier to scale the application by adding or modifying components without affecting the other components.
Reusability: Because the MVC pattern separates an application's concerns, it's easier to reuse components in other applications.
Testability: Because the model, view, and controller are separate components, it's easier to write unit tests for each component.
Conclusion
The MVC pattern is a powerful tool for developing maintainable, modular, and scalable applications. By separating an application's concerns into three distinct components, the MVC pattern makes it easier to develop, test, and maintain applications. Additionally, the MVC pattern provides several advantages, including separation of concerns, scalability, reusability, and testability. If you're a software developer, it's essential to understand the MVC pattern and how to apply it to your projects.